
When designing heating systems, the coolant in which water acts is often necessary to specify the volume of the coolant in the heating system. Such data is sometimes necessary to calculate the volume of the expansion tank relative to the already known power of the system itself.
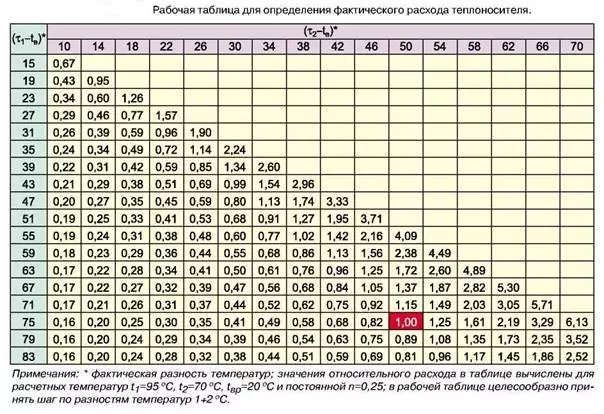
Table to determine the flow of the coolant.
In addition, it is often necessary to calculate this very power or to look for the minimum necessary to know whether it is capable of maintaining the necessary thermal regime in the room. In this case, it is necessary to calculate the coolant in the heating system, as well as its expense per unit of time.
Choosing a circulation pump
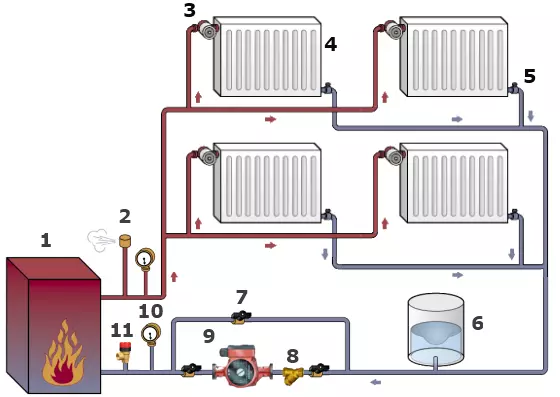
Circulating pump installation circuit.
The circulation pump is an element without which it is even difficult to imagine any heating system, it is selected by two main criteria, that is, two parameters:
- Q is the coolant consumption in the heating system. Expressed consumption in cubic meters in 1 hour;
- H - pressure, which is expressed in meters.
For example, q to indicate the coolant consumption in the heating system is used in many technical articles and some regulatory documents. Some manufacturers of circulation pumps are used to designate the same consumption. But the plants for the production of shut-off valves as the designation of the coolant consumption in the heating system use the letter "G".
It is worth noting that the above designations in some technical documentation may not coincide.
Immediately it is necessary to make a reservation that in our calculations to designate the flow, the letter "Q" will be applied.
Calculation of the flow rate of the coolant (water) in the heating system
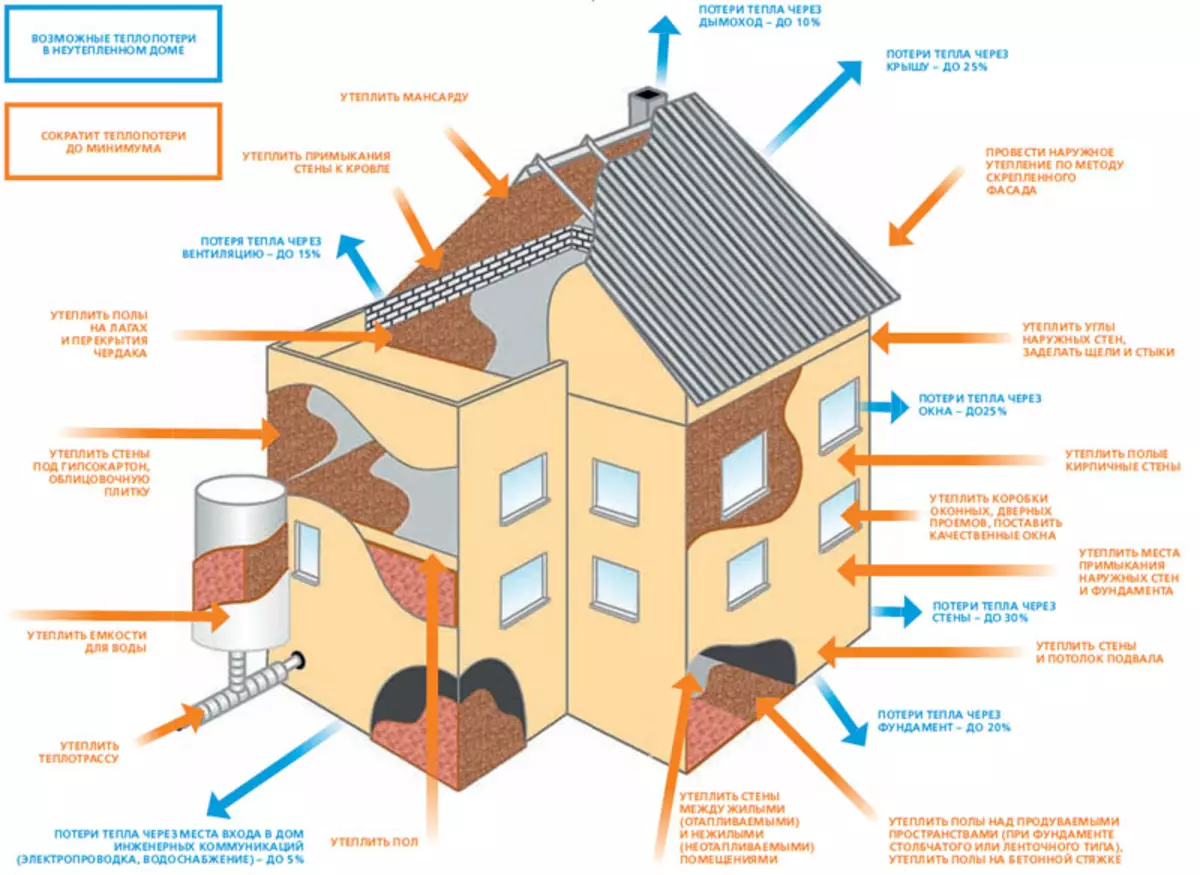
The heat loss of the house with insulation and without.
So, to choose the right pump, you should immediately pay attention to such a magnitude as the heat loss at home. The physical meaning of the connection of this concept and pump is as follows. A certain amount of water heated to a certain temperature is constantly circulating through pipes in the heating system. Circulation exercises pump. At the same time, the walls of the house constantly give part of their heat into the environment - this is the thermal loss of the house. It is necessary to know how minimal amount of water should pump a pump on the heating system with a certain temperature, that is, with a certain amount of thermal energy, so that this energy is enough to compensate for heat losses.
In fact, when solving this task, the pump bandwidth is considered, or water consumption. However, this parameter has a slightly different name for the simple reason, which depends not only on the pump itself, but also on the temperature of the coolant in the heating system, and in addition, from the bandwidth of the pipes.
Taking into account all the above, it becomes clear that before the main calculation of the coolant, it is necessary to make the calculation of thermal loss of the house. Thus, the calculation plan will be as follows:
- finding thermal loss of the house;
- establishment of the average temperature of the coolant (water);
- Calculation of the coolant in binding to water temperature relative to thermal loss of the house.
Calculation of heat loss
This calculation can be made independently, since the formula has long been removed. However, the calculation of the heat consumption is quite complex and requires consideration of several parameters at once.If we say simply, it only comes down to determine the loss of thermal energy, expressed in the power of the heat flux, which each square M of the area of walls, floors, floor and roofs radiate into the external environment.
Article on the topic: Fiber for screed: Consumption for 1m3, how much to add
If you take the average value of such losses, they will be:
- about 100 watts per unit area - for average walls, such as brick walls of normal thickness, with normal interior decoration, with double double-glazed windows;
- more than 100 watts or significantly more than 100 watts per unit area, if we are talking about the walls with insufficient thickness, disgraced;
- About 80 watts per unit area, if we are talking about walls with sufficient thickness having an outer and internal thermal insulation, with installed double-glazed windows.
To determine this indicator, a special formula is derived with greater accuracy, in which some variables are tabular data.
Accurate calculation of thermal loss of the house
For a quantitative indicator of thermal loss of the house there is a special value, which is called a heat flux, and it is measured in kcal / hour. This value physically shows heat consumption, which is given to the walls in the environment with a given thermal mode within the building.
This value depends directly from the architecture of the building, from the physical properties of wall materials, gender and ceiling, as well as from many other factors that can cause weathering of warm air, for example, an improper device of the heat-insulating layer.
So, the magnitude of the thermal loss of the building is the sum of all thermal losses of its individual elements. This value is calculated by the formula: G = S * 1 / Po * (Two) to, where:
- G - the desired value expressed in kcal / h;
- Po - resistance to the heat exchange process (heat transfer), expressed in kcal / h, this is sq.m * h * temperature;
- TV, TN - air temperature indoors and outside, respectively;
- K is a reducing coefficient, which for each thermal barrier is its own.
It is worth noting that since the calculation is done not every day, and in the formula there are temperature indicators that change constantly, then such indicators are taken in averaged form.
This means that the temperature indicators are taken average, and for each individual region, this indicator will be its own.
So, now the formula does not contain unknown members, which allows to carry out a fairly accurate calculation of thermal loss of a particular home. It remains to know only the downward coefficient and the value of the Po resistance value.
Both of these values depending on each specific case, you can learn from the corresponding reference data.
Some values of the downstream coefficient:
- Paul in soil or wooden lagas - value 1;
- The overlaps are attic, in the presence of a roof with a roofing material of steel, tiles on a rarefied cladder, as well as the roof from asbestoscerta, an inscredit coating with ventilation, is 0.9;
- The same overlaps, as in the previous paragraph, but arranged on a solid flooring, is 0.8;
- Overlapping is attic, with the roof, which is roofing material of which is any rolled material - value of 0.75;
- Any walls that share a heated room with unheated, which, in turn, has an outer wall, is 0.7;
- Any walls that share a heated room with unheated, which, in turn, does not have outer walls, is 0.4;
- The floors arranged above the cellars located below the level of the outdoor soil - the value of 0.4;
- The floors arranged above the cellars located above the level of the outdoor soil - the value of 0.75;
- The overlaps, which are located above the basement, which are located below the level of the outer soil or higher at a maximum of 1 m, is 0.6.
Article on the topic: Decorating the curtains of the remnants of Tulle and sew Useful little things: master class
Based on the above cases, it is possible to approximately imagine the scale, and for each specific case that did not enter this list, select the downward coefficient yourself.
Some values for heat transfer resistance:
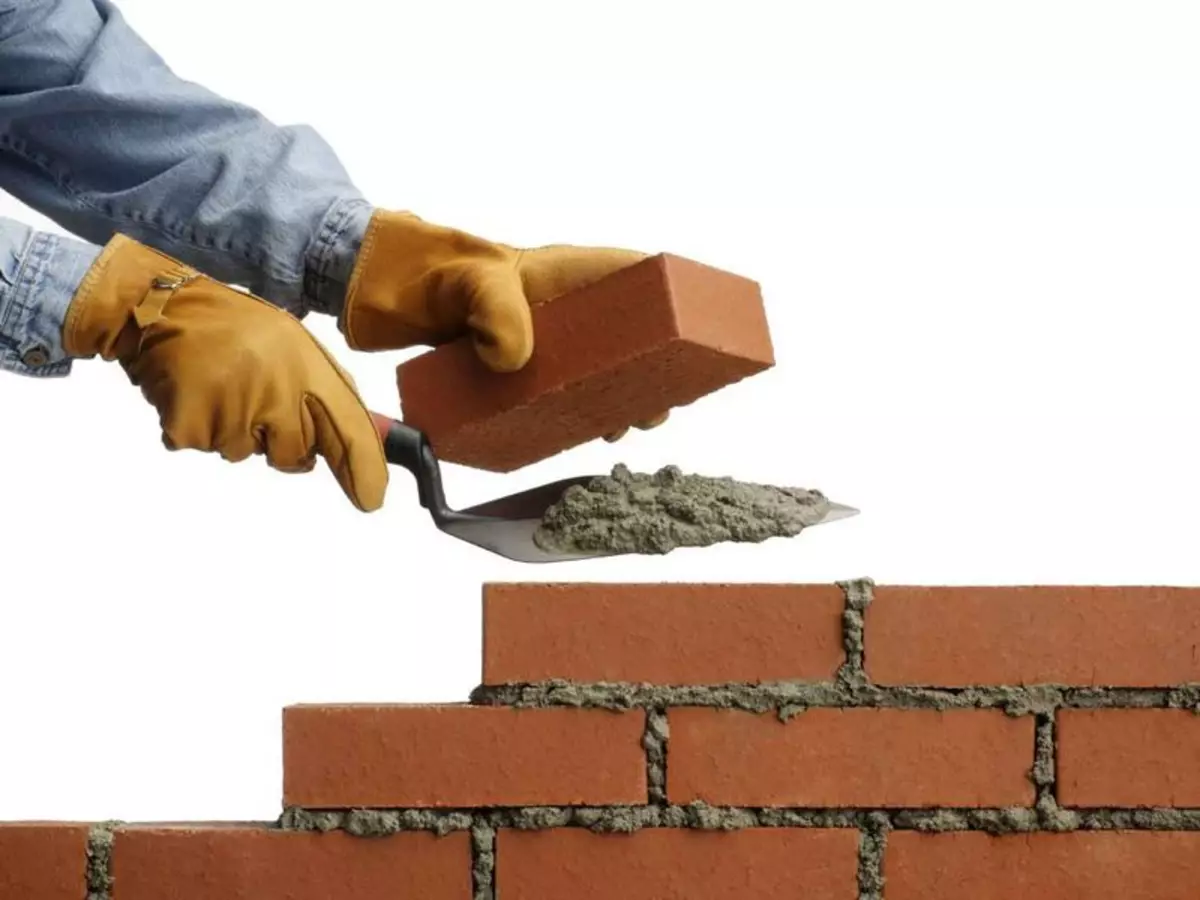

The resistance value for solid brick masonry is 0.38.
- For conventional solid brickwork (the wall thickness is approximately equal to 135 mm) the value is 0.38;
- The same, but with a thickness of masonry in 265 mm - 0.57, 395 mm - 0.76, 525 mm - 0.94, 655 mm - 1.13;
- For solid masonry having an air layer, with a thickness of 435 mm - 0.9, 565 mm - 1.09, 655 mm - 1.28;
- For solid masonry made of decorative bricks for a thickness of 395 mm - 0.89, 525 mm - 1.2, 655 mm - 1.4;
- For solid masonry with a thermal insulation layer for a thickness of 395 mm - 1.03, 525 mm - 1.49;
- For wooden walls from individual wooden elements (not timber) for a thickness of 20 cm - 1.33, 22 cm - 1.45, 24 cm - 1.56;
- For walls from a bar with a thickness of 15 cm - 1.18, 18 cm - 1.28, 20 cm - 1.32;
- For an attic ceiling of reinforced concrete plates with the presence of a heater with a thickness of 10 cm - 0.69, 15 cm - 0.89.
Having such tabular data, you can proceed to accurate calculation.
Direct calculation of the coolant, pump power
We accept the magnitude of thermal losses per unit area equal to 100 watts. Then, having accepted the total area of the house, equal to 150 sq. M, it is possible to calculate the total thermal loss of the entire house - 150 * 100 = 15000 watts, or 15 kW.
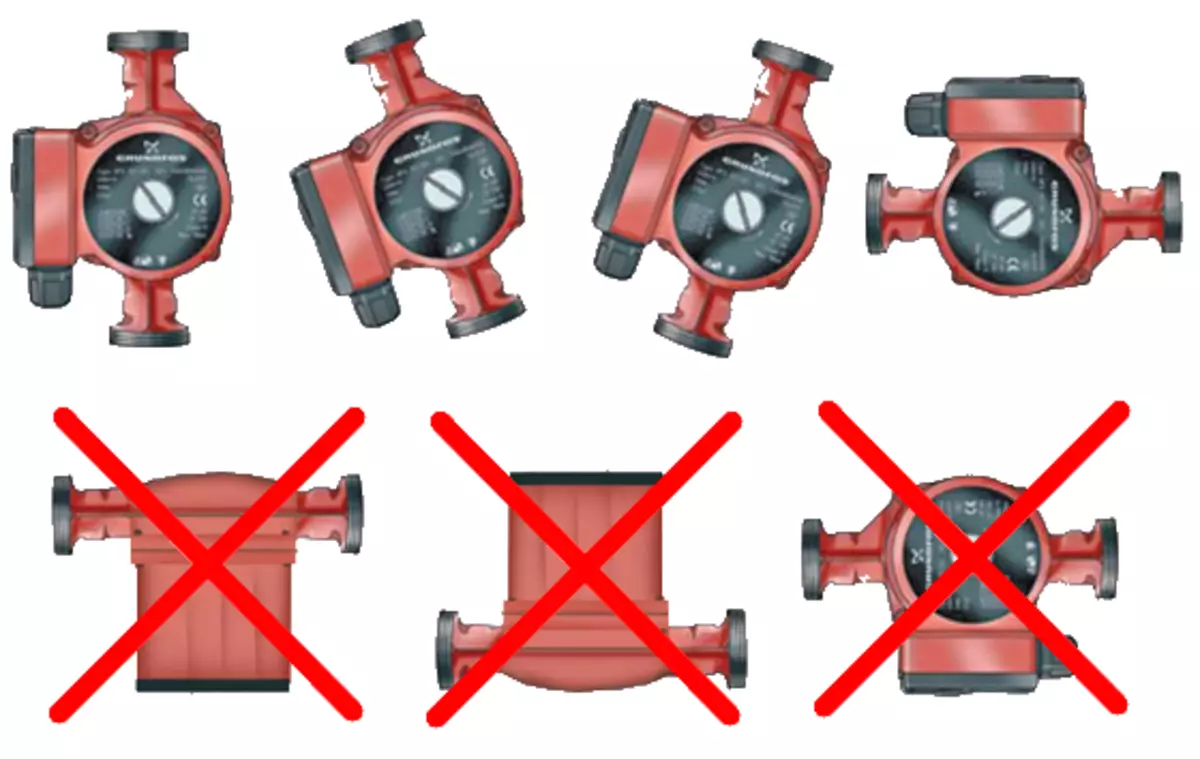
The operation of the circulation pump depends on its proper installation.
Now it should be sorted out what kind of number this figure has to the pump. It turns out the most direct. It follows from physical sense that thermal losses are a constant process of heat consumption. To keep indoors the necessary microclimate, it is necessary to constantly compensate for such a consumption, and to increase the temperature in the room, you must not just compensate, but to produce more energy than you need to compensate for losses.
However, even if there is thermal energy, it still needs to be delivered to the device that can dispel this energy. Such an appliance is a heating radiator. But the delivery of the coolant (energy owner) to radiators is carried out by the circulation pump.
From the foregoing, it can be understood that the essence of this task comes down to one simple question: how many water is heated to a certain temperature (that is, with a certain heat of thermal energy), it is necessary to deliver to radiators for a certain period of time to compensate for all thermal losses at home ? Accordingly, the answer will be obtained in the volume of water pumped water per unit of time, and this is the power of the circulation pump.
To answer this question you need to know the following data:
- The required amount of heat that needs to compensate for thermal losses, that is, the outcome of the calculation above. For example, 100 watt value was taken at 150 square meters. m, that is, in our case, this value is 15 kW;
- The specific heat capacity of water (this is reference data), whose value is 4,200 joule energy per kg of water for each degree of its temperature;
- The temperature difference between that water that comes out of the heating boiler, that is, the initial temperature of the coolant, and the water that enters the boiler from the return pipeline, that is, the final temperature of the coolant.
Article on the topic: Window design: Classification and features
It is worth noting that with a normally running boiler and the entire heating system, with normal water circulation, the difference does not exceed 20 degrees. As an average, you can take 15 degrees.
If you consider all the above data, the formula for calculating the pump will take the form Q = G / (C * (T1-T2)), where:
- Q is the flow of coolant (water) in the heating system. It is such an amount of water at a certain temperature mode, a circulation pump should be delivered to the radiators per unit of time to compensate for the thermal losses of this house. If you purchase a pump that will have much more power, it will simply increase the consumption of electrical energy;
- G - thermal losses calculated in the previous paragraph;
- T2 - water temperature that follows from the gas boiler, that is, the temperature to which it is required to heat a certain amount of water. As a rule, this temperature is 80 degrees;
- T1 - The temperature of the water that flows into the boiler from the return pipeline, that is, the water temperature after the heat transfer process. As a rule, it is equal to 60-65 degrees.;
- C - the specific heat capacity of water, as already mentioned, it is equal to 4,200 joule on kg of coolant.
If we substitute all the data obtained in the formula and convert all the parameters to the same measurement units, then we obtain the result of 2.4 kg / s.
Translation of the result to normal
It is worth noting that in practice this consumption of water will not meet anywhere. All water pump manufacturers express the pump power in the cubic meters per hour.Some transformations should be made, remembering the school physics. So, 1 kg of water, that is, the coolant, it is 1 cu. DM water. To find out how much one cubic meter weighs, you need to know how many cubic decimeters in one cubic meter.
Using some simple calculations or simply using tabular data, we obtain that in one cubic meter contains 1000 cubic decimeters. This means that one cubic meter of the coolant will have a mass of 1000 kg.
Then in one second you need to pump water in 2.4 / 1000 = 0.0024 cubic meters. m.
Now it remains to translate seconds to hours. Knowing that in one hour 3600 seconds, we obtain that in one hour the pump should pump 0.0024 * 3600 = 8.64 cubic meters / h.
Summarizing
So, the calculation of the coolant in the heating system shows how much water is required by the entire heating system to maintain the house room in normal temperature mode. The same figure is conditionally equal to the power of the pump, which, in fact, will carry out the delivery of the coolant to radiators, where it will give part of its thermal energy into the room.
It is worth noting that the average power of pumps is approximately 10 cubic meters / h, which gives a small margin, since the heat balance must not only save, but sometimes, at the request of the owner, increase the air temperature, to which, in fact, the additional power is needed. .
Experienced specialists recommend purchasing a pump, which is about 1.3 times more powerful. Speaking about a gas heating boiler, which, as a rule, is already equipped with such a pump, you should pay your attention to this parameter.
