
In the process of selecting thermal insulation materials, structures and products, a number of important issues are inevitable, a number of important questions, which can be correctly replied to which only by performing the appropriate calculations, because other methods (analog method, etc.) are far from all cases give an acceptable result. A simple example: in the case of a non-channel gasket of pipelines with a conditional passage of 200 mm, one only change in the characteristics of the soil and the depth of the embedding can change the minimum possible thickness of thermal insulation by 40% under all other equal conditions. And the value of thermal losses at a fixed thickness of the heat insulating layer may increase by 24%. It follows the conclusion that even with the unchanging parameters of pipelines and coolants, it is necessary to carry out the individual calculation of heat losses, taking into account specific laying conditions.
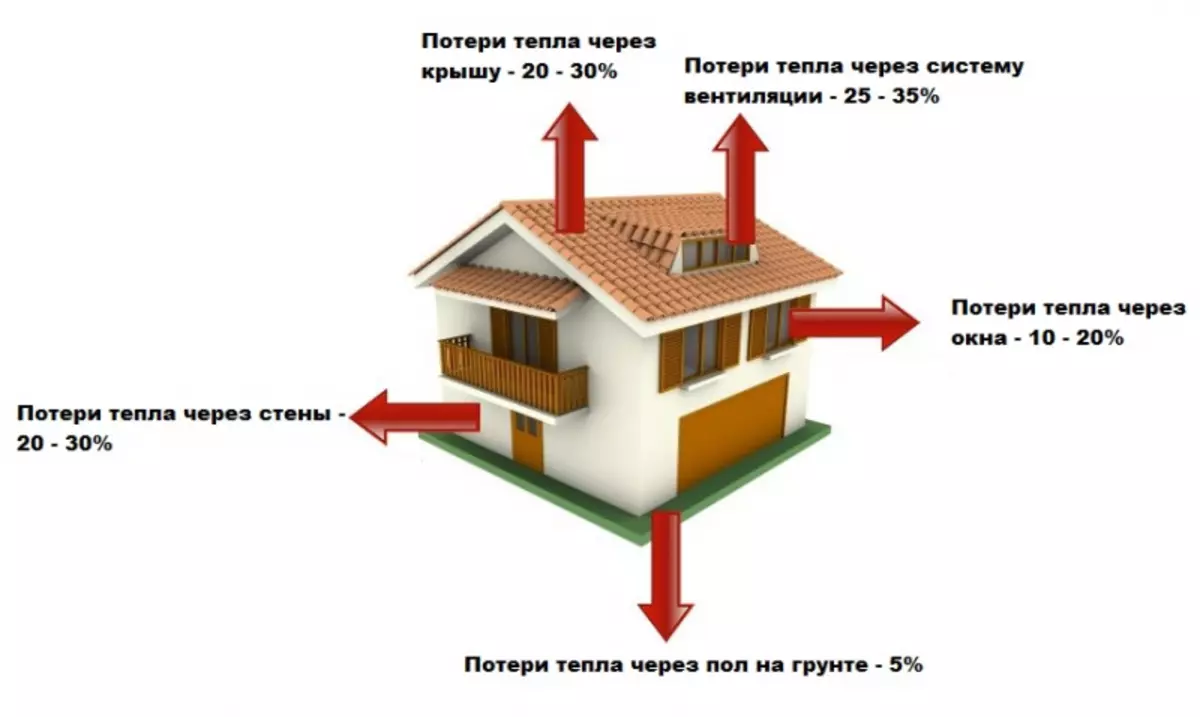
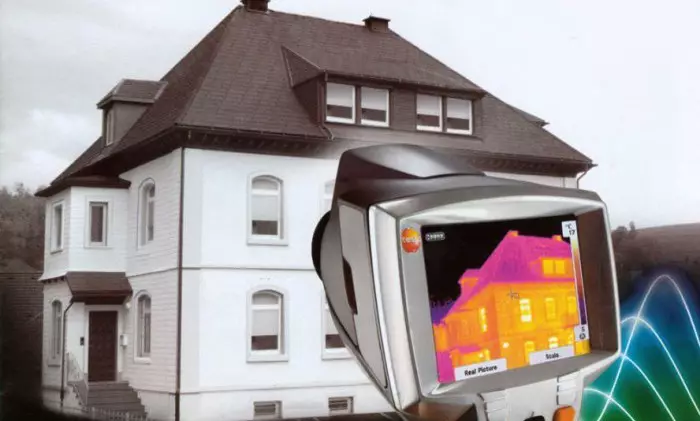
Scheme heat loss at home.
General information about the method of calculating thermal losses
The goal of the calculation of heat losses is to determine the actual losses of heat through the thermal insulation of pipelines of water thermal networks of centralized heat supply.
The calculation of thermal losses is carried out for the entire heating system connected to a common source of energy. The calculation of the actual losses of thermal energy for some separate sections of the network is not performed.
The calculation of thermal losses involves the presence of certified nodes of thermal energy metering both in thermal energy consumers and on the source of thermal energy. The number of consumers having accounting devices should be at least 20% of the total number of consumers under consideration of the thermal network.
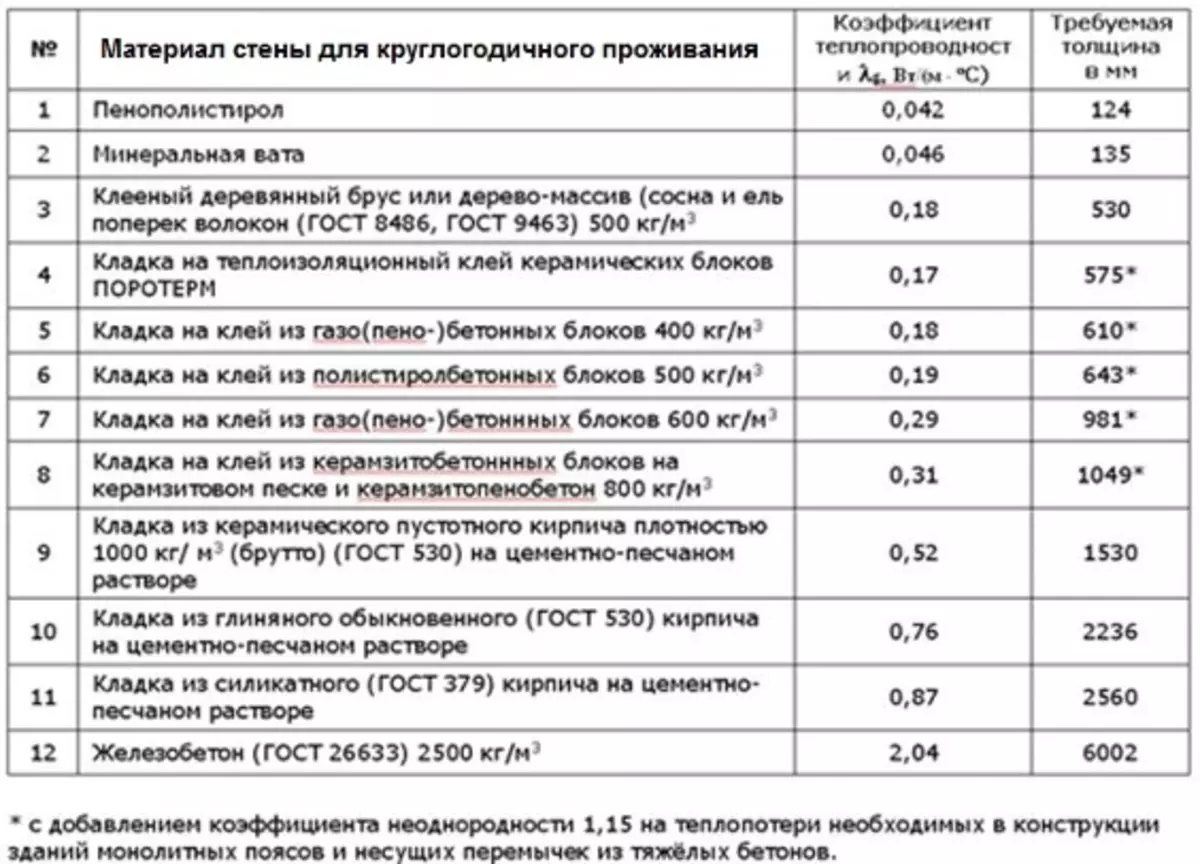
Table of calculation of heat losses.
Devices using which will be calculated by the calculation of heat loss of heating pipelines, must be equipped with an archive clockwise and daily registration of values. The depth of the clock archive should be at least 720 hours, and the daily - no less than 30 days.
The main one when performing the calculation of thermal losses of heating pipelines is an hour archive. The daily archive is used in the absence of time data for any reason.
The calculation of actual heat losses is performed on the basis of temperature measurements and network water flows in the supply pipeline in consumers of a network that have accounting devices, as well as the temperature of the network water at the energy source. The calculation of thermal losses for consumers without measuring instruments is performed by a slightly different methodology.
Consumers and sources of thermal energy are considered:
- In the absence of accounting devices directly in buildings: consumers of thermal energy - individual or central thermal items; sources of thermal energy - boiler houses, thermal power plants, etc.;
- In the case of accounting devices directly in buildings by consumers of thermal energy, the buildings are considered directly, and the sources are central thermal points.
Regulations of the flow of thermal energy to the own needs of the boiler room.
For the convenience of calculating the loss of thermal energy through thermal insulation, feed pipelines are delimited by: the main pipelines and branches from the main pipelines.
Under the main pipeline should be understood as part of the supply pipe between the source of thermal energy and the thermal chamber, which is branched to the consumers of thermal energy.
Branch from the main pipelines is part of the supply pipelines from the corresponding thermal chambers to thermal energy consumers.
Calculation of actual heat losses is carried out using regulatory loss values, which are determined by heat energy loss standards for networks, the thermal insulation of which was performed in accordance with the design standards (the norms should be specified by project and executive documentation).
Preparation for the calculation
Before starting the calculation of heat losses, you need:
- collecting source data on the thermal network under consideration;
- Create a circuit diagram of the heat network, which indicates the conditional diameter (conditional pass), the type and length of the pipeline laying for all sections of the network;
- collect data on the connected load of consumers of the heat network;
- Install the type of accounting devices and the presence of time and daily archives.
Article on the topic: Wealth of ornaments for the facade of the house
Typical calculated diagram of the heat network.
In the absence of a centralized collection of account data data, the necessary devices for collecting are preparing: a portable computer or adapter. On a portable computer, you must install a special program that comes with the accounting instrument. This program is designed to read the time and daily archives from the specified heat meters.
In order to increase the accuracy of the calculation of heat losses, it is preferable to collect account data for some time interval to the ultimate season when the power consumption is insignificant, having previously learned in the heat supply organization about the planned heat supply shutdowns in order for this time to exclude from the period of measuring instrument testimony.
With the help of project and executive documentation under the thermal network under consideration, the table of all sections of this heat network is created. Under the section of the thermal network, it is necessary to understand the pipeline section, which differs from the rest of one of the following characteristics:
- the conditional diameter of the pipeline (conditional passage of the pipeline);
- type of laying (underground channel, overhead, underground chambling);
- thermal insulation (material of the main layer of thermal insulation design);
- The year of the gasket.
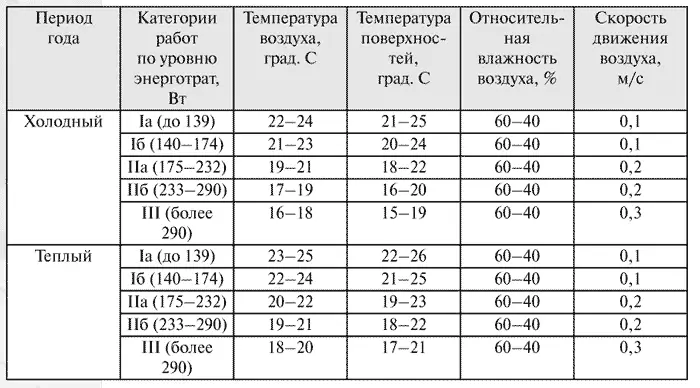
Table of average soil temperature and outdoor air.
The corresponding table additionally indicates the length of the site and the name of the initial and end nodes of the area under consideration.
Based on the data of the meteorological service, it is necessary to draw up a table of average soil temperatures and outdoor air at different depths of gasket pipelines averaged for 5 years. The average annual soil and outdoor temperatures are defined as the arithmetic average of average average values for the entire operation time of the thermal network. Based on the approved heat schedule of heat energy, it is necessary to determine the average monthly temperature of the network water in the opposite and feed pipelines.
To determine the average monthly temperature of the network water, you need to know the average temperature of the outer air. The average annual temperature of the network water in reverse and supply pipelines is defined as the arithmetic average of the average monthly indicators, taking into account the duration of the thermal network for months and for the calendar year. Based on the process of conducting heat consumption, which can be obtained in a heat supply organization, you should draw up a table in which the following data are given for each consumer:

The calculated values of the consumption of network water for hot water supply.
- type of heat supply system (closed or open);
- The name of consumers of thermal energy;
- Attached load of the ventilation system;
- Attached load of the heating system;
- The value of the connected average load of the hot water system;
- Depth of the hour and daily archives;
- brand (name) accounting devices;
- The absence or presence of a central data collection.
If you have a centralized data collection in accordance with the measurement results, you should choose the period for which the calculation of thermal losses will be performed. At the same time, a number of factors should be taken into account, namely:
- In order to increase the accuracy of the calculation of heat losses, it is best to choose a period with the smallest consumption of network water (as a rule, this is an urgent period);
- In the selected period of time, the planned disclosures of consumers from the heating network should not be carried out;
- Measuring instrument indicators are collected at least 30 calendar days.

The formula for calculating heat losses.
In the absence of a centralized data collection, you need to collect the daily and clock archives of accounts in consumers of heat and at the heat source, using the adapter or a portable computer with the installed data to read data from the heat meter installed for this.
To calculate thermal losses, you need to have the following data:
- The temperature of the power water in feed pipelines in consumers;
- Consumption of network water in feed pipelines in consumers;
- The temperature of the power water in reverse and supply pipelines on the source of heat;
- The consumption of network water in supply pipelines on the source of heat;
- Consumption of feeding water at the source of energy.
Article on the topic: Sequins for wallpaper: Attractive interior
Procedure for processing the source data of accounting devices
The main task of processing account data is to convert the source files that are read directly from heat meters into a single format that allows you to conduct further verification for the accuracy (verification) of the measured parameters of heat consumption and the necessary calculations.
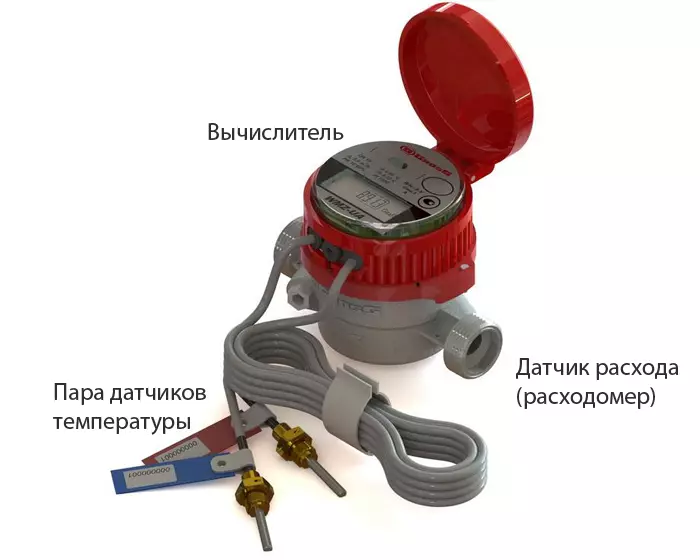

The design of the heat meter.
For thermal counters of different types, data is read in different formats and require relevant processing procedures. So, for one type of heat meters from various consumers, the parameters stored in the archive may require the use of different coefficients of bringing initial data to single physical quantities. The difference in these coefficients is determined by the characteristic of the pulse store inputs and the flow converter diameter. In view of this, the initial processing of the data obtained requires an individual approach for source data files. The time and daily coolant parameters are used to confirm the accuracy of the measured values. When performing this procedure, it must be focused on the following indicators:
- The value of the costs and temperatures of the coolant should not be out of physically reasonable boundaries;
- The daily file should not contain sharp changes in the coolant consumption;
- Changing the value of the average daily temperature of the carrier in the supply pipe at the source of thermal energy should correspond to the change in the average temperature in the supply pipeline and consumers;
- The average daily temperature of the coolant in the supply pipeline in consumers must not be higher than the average daily temperature values in the feed pipe on the source.
The design of the heat meter.
In accordance with the results of verification of the initial data, accounting probits should be a table in which for all thermal energy consumers having accounting devices, and for the energy source is given that period of time when the accuracy of the initial data is not in doubt. Based on this table, select a total period during which there are reliable changes for all network consumers and the source of heat (the so-called data availability).
Based on the time file of the data obtained at the heat source, determine the number of hours in the measurement period, data for which will be used for further processing. Before determining the measurement period, you should calculate the time required to fill all feed pipelines with the coolant.
Conditions for calculation
It is necessary that the measurement period will satisfy a number of conditions, namely:
- The value of the average temperature of the network water in the supply pipe at the heat source during the time before the measurement period and the value of the average water temperature in the supply pipe at the heat source during the end of the measurement should be different than 5 degrees;
- Measurements should be carried out continuously for at least 240 hours;
- The measurement period should be fully contained in the presence of data.
Calculation of the heat loss of the house.
If such a period cannot be selected due to the lack of data from one or several consumers, then these consumer accounting instruments are not used in future calculations.
The number of consumers who have accounting instruments data should be at least 20% of the total number of consumers under consideration of the thermal network. In the event of a decrease in the number of consumers with accounting devices up to less than 20%, it is necessary to select another period for data collection and again do the verification procedure.
For the parameters obtained on the heat source, it is necessary to determine the average for the measurement period of the power water temperature in the supply pipeline and the average for the measurement period the temperature of the network water in the return pipeline.
For the measuring period, it is necessary to determine the average air temperature and the average temperature of the soil on the middle depth of the axis of pipelines.
Method of calculating the characteristics of thermal insulation
The calculation of the minimum allowable thickness of thermal insulation of pipelines and equipment is performed on the basis of the heat flux density norms that are fixed in SNiP 41-30-2003. The algorithm and calculation formulas are given in SP 41-103-2000. With the help of the same document, actual thermal losses can be calculated.Article on the topic: Fire doors GOST 31173 2003
However, the problem lies in the fact that, depending on the laying option, the number of formulas used for calculations will be from 8 to 23. The number of variables included in them and coefficients - from 20 to 29. So even if you have special knowledge and Experience in performing the calculation of the minimum allowable thickness of thermal insulation (as well as the calculation of actual heat losses) is a very laborious job.
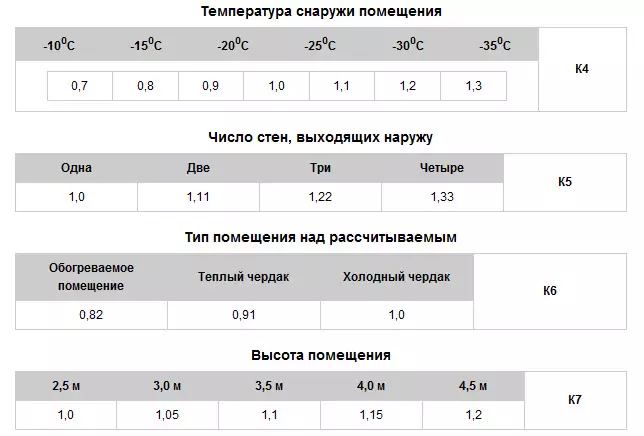
Methods for calculating the minimum allowable thickness of thermal insulation

The formula for calculating the minimum allowable thickness of thermal insulation.
The minimum allowable thickness of thermal insulation of pipelines is determined by the maximum allowable values of heat losses for a unit of pipeline length. These norms are regulated by SNiP 41-03-2003.
Many are interested in what will happen if neglecting the stands of SNiP and allow large thermal losses. If you leave the administrative and legal aspect of this issue aside and consider extremely economic consequences, then it will be as follows.
In recent years, a planned tightening of the Supervisory Approach to consider and approved by the indicators of technologically determined heat losses during energy transportation is occurring. That is, every year, heat supply organizations may include in the tariff (and thereby shift on the shoulders of consumers) all smaller thermal losses.
In accordance with the current regulatory documents, the loss, which are included in the tariff, cannot be larger than the definition of the values more than a certain value that is rigidly regulated. As a rule, this value is limited to additional heat lines through pipelines supports and is about 15-20% of the regulatory losses.
The table of calculation of the minimum allowable thickness of thermal insulation.
The heat loss standards of SNIVA from 2003 are about 26% less than the abandonment standards of 1988, and almost 2.5 times less than the values established by the norms of 1959. It becomes clear that the albums of design solutions and other project documentation, compiled before 2003, are mainly not able to ensure compliance of heat loss with modern requirements.
Thus, the use of obsolete (specifically in this case - developed until 2003) of project decisions or the use of ready-made heat-insulating products without performing calculations for compliance with their requirements SNiP can turn into annual excessive losses of thermal energy.
Method of calculating the actual loss of thermal energy through insulating material
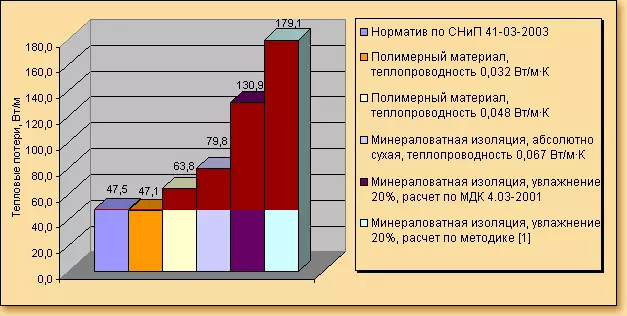
The ratio of the calculated density of the heat flux.
It is impossible to compare different thermal insulation materials and products by the ratio of their price and quality, without determining in advance, what are the values of thermal losses when applied.
The diagram represented in the image 1 shows the ratio of the calculated density of the heat flux when using a variety of thermal insulation materials. With an equal insulation thickness, the thermal flow through it for different materials is different many times. The technique [1] corresponds to the calculation that N.N. Arefyev and L.I. Munyabin.
This diagram shows a thermal stream for products with an equal thickness of the heat insulation material. Theoretically, the higher the value of the thermal conductivity of the material, the thicker should be made from it the product. However, in real conditions, products having greater thermal conductivity, often have a smaller thickness compared to made of more efficient materials. In view of this, in practice, actual heat loss through the insulation of different brands differ even more than on the diagram.
Hence the conclusion, in accordance with which it follows that the economically reasonable selection of thermal insulation products and materials is possible solely on the basis of the results of the calculation of the heat loss, which will occur when the use of these products and materials.
Methods, according to which the calculation of thermal losses through isolation can be performed, there is quite a lot. The main difference between them consists in the methods of accounting for changes in the conditions of operation of heatpets, first of all, the dependences between the thermal conductivity and the moisture absorption of the heat-insulating material.
